CSIR-CGCRI
 CSIR-CENTRAL GLASS AND CERAMIC RESEARCH
INSTITUTE (CSIR-CGCRI)
CSIR-CENTRAL GLASS AND CERAMIC RESEARCH
INSTITUTE (CSIR-CGCRI)
About Organizer of the 27th International Congress on Glass (ICG 2025)
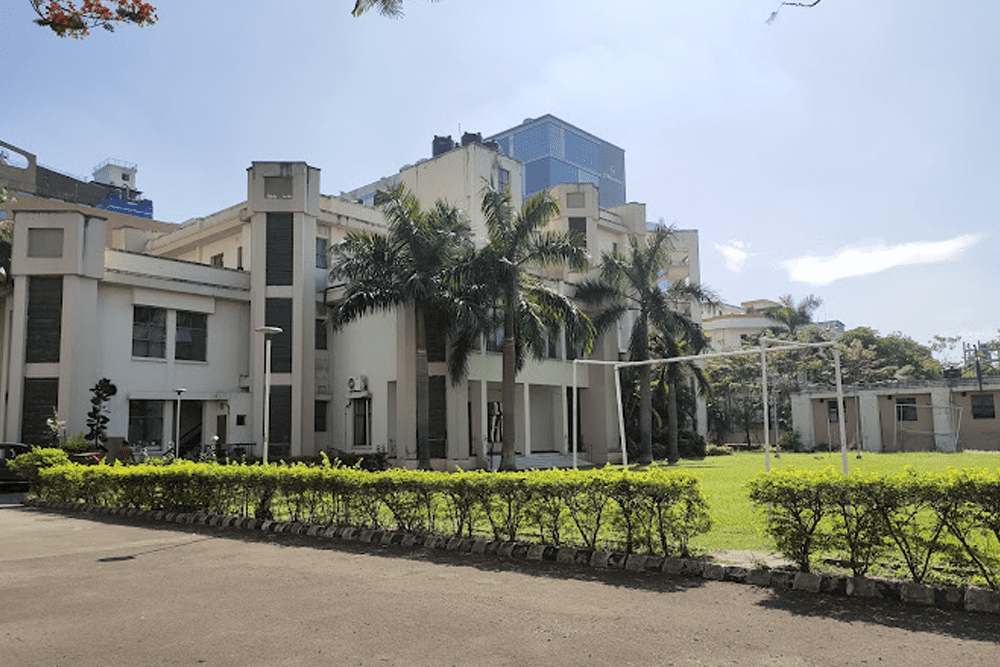
CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute (CSIR-CGCRI) is one of the first four laboratories that was set up under CSIR. Though it started functioning in a limited way in 1944, the Institute was formally inaugurated on August 26, 1950. In order to serve the local industrial clusters, the Institute established two extension centres at Naroda (Gujarat, India) and Khurja (UP, India). Presently, CSIR-CGCRI has a large pool of highly experienced and dedicated scientists of about 100 working in various fields of glass and ceramics research who are assisted by about 150 technical staff and a few hundred-research students. CSIR-CGCRI came into limelight by developing the technology for production of optical glass with a view to making the country self-reliant and consequently established an optical glass pilot plant with an annual capacity of 10 tonnes in 1961 without any foreign collaboration. In the seventies, the Institute initiated the development of laser glass, infrared transmitting filters, and synthetic quartz single crystal. All these carry the testimony of CSIR-CGCRI to become the leader in glass and ceramic research in the country. In the eighties CSIR-CGCRI started work on a number of fields, some of which were even in their nascent stage in the international arena. Work in the field of optical fibre for telecommunications, sol-gel processing of glass and ceramic materials, production of glass fibre based composites and application of ceramic materials in electronics were initiated during this period. Over the years, Glass Division of CSIR-CGCRI has developed various glasses and glass-ceramics namely radio-photoluminescent (RPL) glass, filter glass, colored signal glass, lanthanum bearing optical glass, radiation shielding window (RSW) glass, glasses for nuclear waste immobilization, rare-earth doped luminescent glass, tellurite glass, transparent nano-crystalline and machinable glass-ceramics etc. for several niche applications. Currently, R & D activities have been diversified in the areas of chalcogenide glass, bioactive glass, oxyfluoride glass-ceramics, nonlinear optical glass-ceramics, etc. to fulfil countries requirements as well as for emerging applications. Similarly, Fiber Optics and Photonics Division has made immense contributions in the fields of fiber amplifiers, high power fiber lasers, photonic crystal fibers and fiber Bragg grating sensors for practical applications. The Congress is being planned in association with the major glass and ceramic societies in India such as Indian Ceramic Society, All India Glass Manufacturers Federation and Glazing Society of India.
Read More









 27th International Congress on Glass
27th International Congress on Glass Indian Ceramic Society (InCerS)
Indian Ceramic Society (InCerS) All India Glass
Manufacturers' Federation (AIGMF)
All India Glass
Manufacturers' Federation (AIGMF) Glazing Society of India
Glazing Society of India